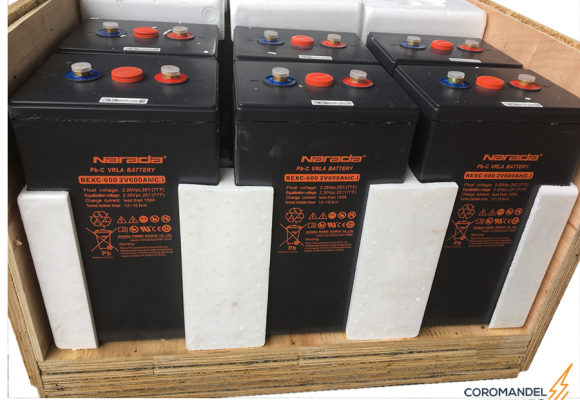
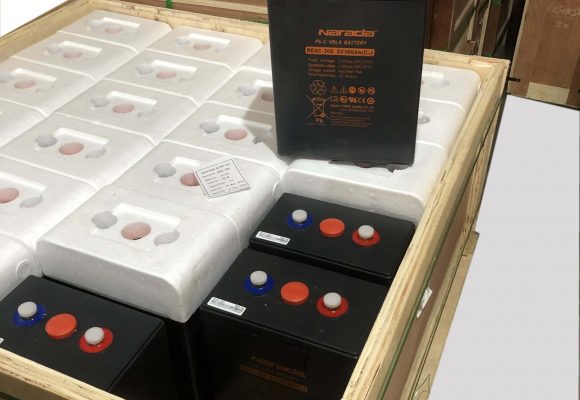
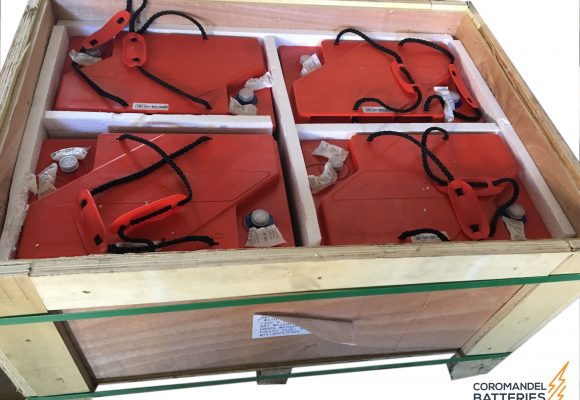
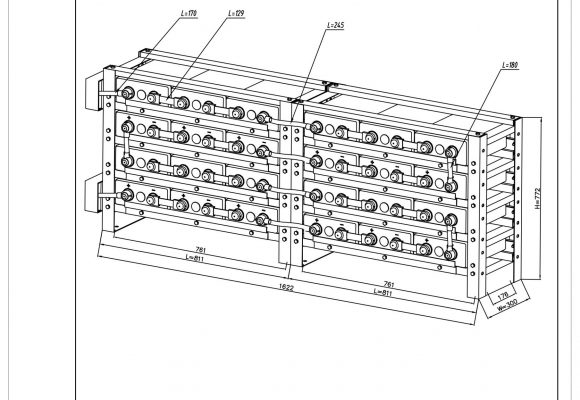
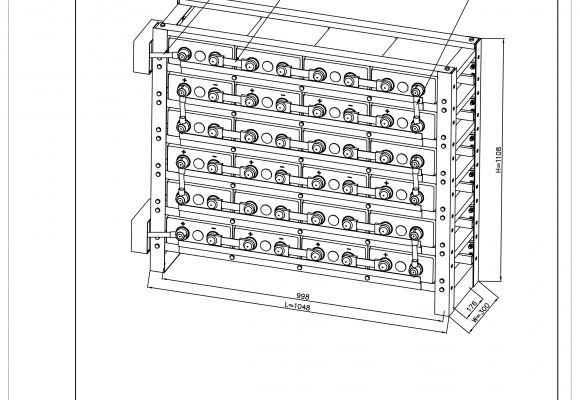
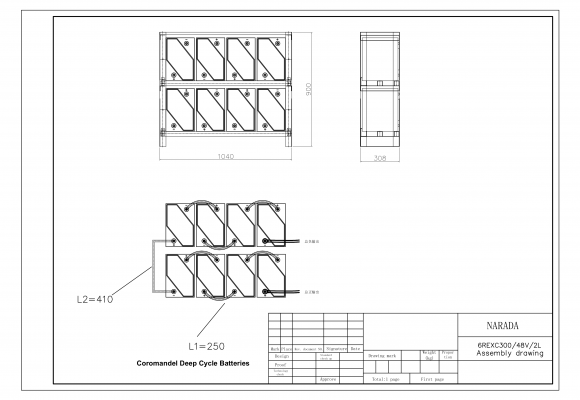
All battery sets are supplied in palletised plywood crates of either 4 (6REXC-300), 12 (REXC-600 & REXC-1000) or 24 batteries (REXC-300). They are well packed to allow for sea and road freight transport and can be lifted by forklift or pallet lifters.
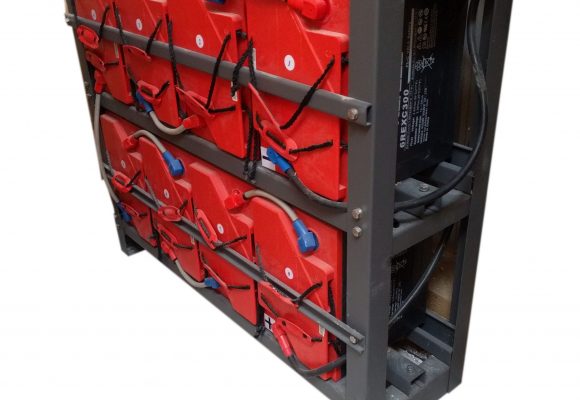
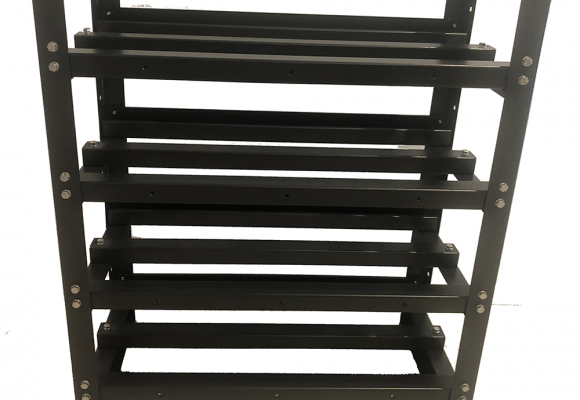
Narada REXC lead-carbon batteries are sealed valve regulated lead acid (VRLA) batteries that can be installed in any orientation. If your batteries are supplied with a Narada racking system then they will be mounted into the rack with the terminals facing out (i.e. on their side). Without a rack it is possible to sit the batteries upright on the floor (preferably an insulated floor to help maintain an even temperature) or in a home made rack.
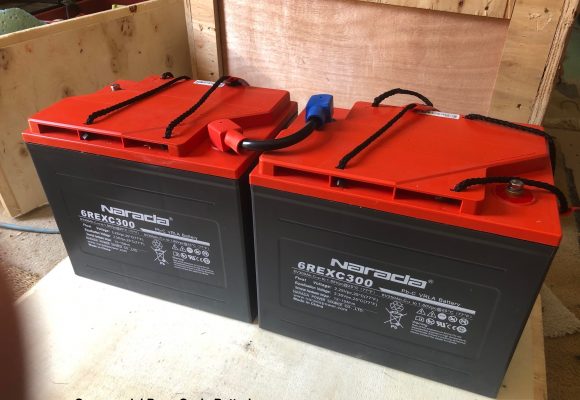
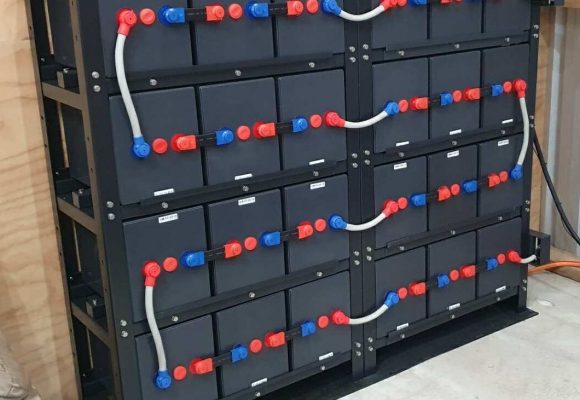
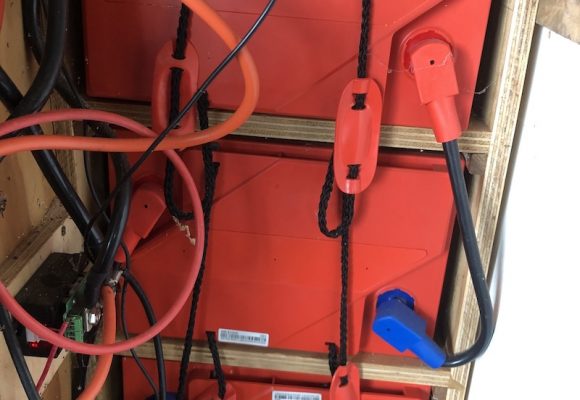
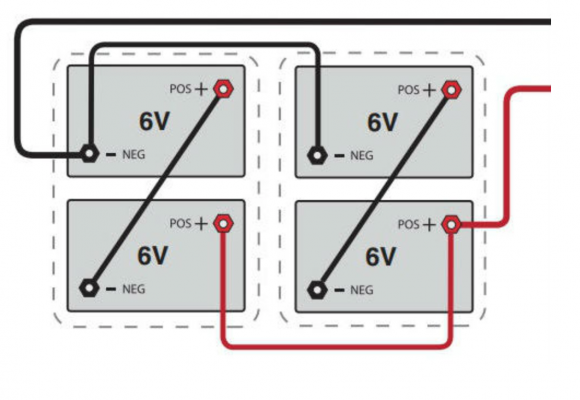
Battery sets supplied with a rack also come with solid copper links to connect the +ve and -ve terminals of adjacent batteries and flexible cables to go between layers. Batteries supplied without a rack include flexible cables for all connections. Supplied cables are sized appropriately for each battery type – 25mm2 for 6REXC-300, 35mm2 for REXC-300, 70mm2 for REXC-600 and 90mm2 for REXC-1000.
48V rack sets for 2V REXC series batteries are also supplied with large terminal block that is attached to the side of the rack at the -ve and +ve terminals of the set. This has extra 8mm studs that can be used to connected multiple heavy duty cables if you have a longer than usual run of cable to the battery bank and need to run two cables in parallel to achieve the appropriate minimum voltage drop. Because of the high currents present with large battery banks (in excess of 100 amps for REXC-600 and REXC-1000 batteries) it is important that you use correctly sized cables. However it is sometimes more economical to use two 35mm2 cables in parallel rather than a single 70mm2 cable for example.
VRLA batteries do not give off irritating or explosive gases during normal use, but they must still be installed in an adequately ventilated space so that in the event of malfunction (including overcharging) gases can be safely dispersed. Installation of battery banks must be in compliance with the standard AS/NZS 5139:2019 “Electrical Installations – Safety of battery systems for use with power conversion equipment”. This states that batteries must not be installed in a habitable space but can be installed in areas such as garages or utility areas inside a house, as well as in specially built battery rooms, on verandahs or outside in battery sheds. If installed in a garage the battery area must be protected from damage (by a car running into it for example) and must be separated within the garage. The AS/NZS 5139 is $150 + GST to purchase but you can read a draft of the standard via the link to the right.
As explained in the Lifespan section, it is important for long life that batteries are kept as close as possible to a temperature range of 15 to 25 °C. They should therefore not be installed in an outside shed or lean-to on the northern or sunny side of a building where they will almost certainly get warmer than 30 °C in summer. Batteries age twice as fast for every 10 °C increase in operating temperature above 25 °C. An air gap should be maintained between individual batteries (10 to 15mm) to allow natural cooling and prevent heat buildup. If you have a rack mount system the batteries will be spaced correctly by the rack and connecting links.